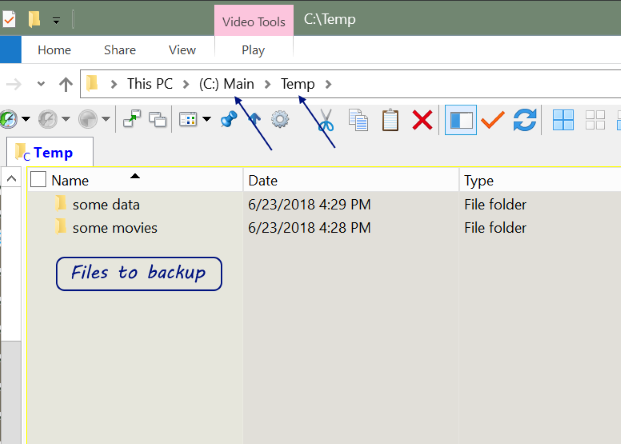
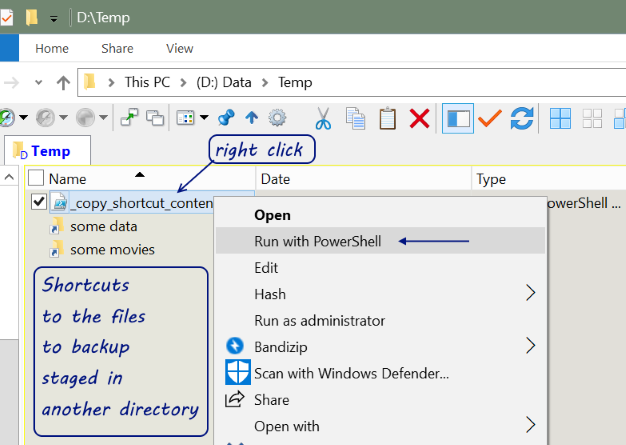
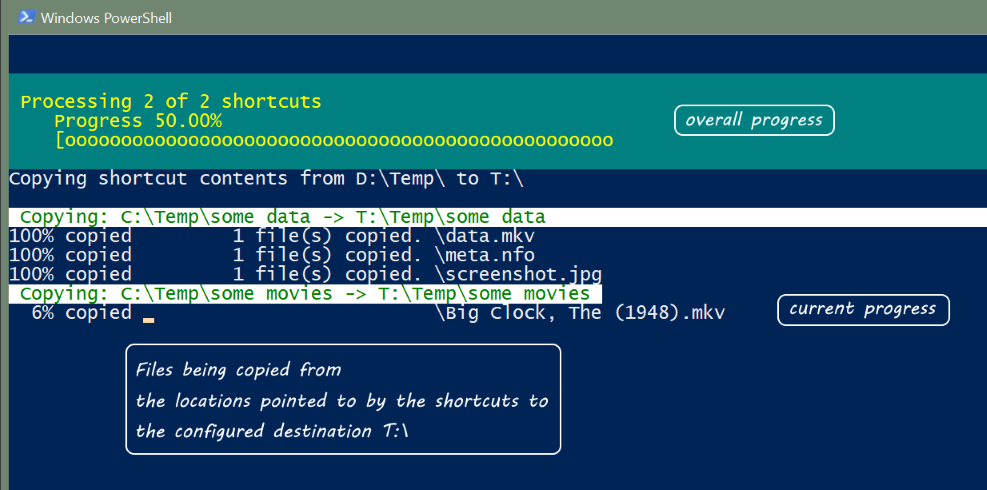
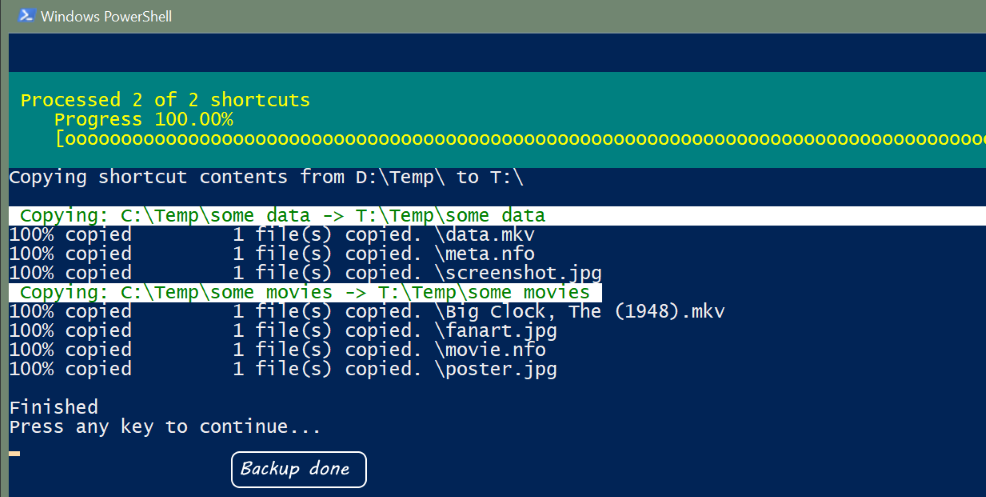
When you view a website page or make a request against an application api, HTTP headers allow the client and the server to pass additional information with the request, page content, or the response.
Typical HTTP headers sent are Host, Accept-Language, etc, while typical HTTP headers received are Content-Type, Server, Content-Security-Policy, etc
You can view HTTP Headers using the browsers developer tools in
Chrome or
Firefox.
HTTP Security Headers are a subset of HTTP headers which can help increase the security of your web application and website. In many cases they are easy to implement and only require a slight web server configuration or application change.
For the additional security to be realized, the browser must support the HTTP Security Headers, which most modern browsers do.
Can I Use and
Mozilla are both good sites to see what features browsers support.
HTTP Security Headers to implement:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin Mozilla
Indicates whether the response can be shared with requesting code from the given origin.
Possible values:
*
- allow requesting code from any origin to access the resource
https://example.com/
- one domain
Recommended:
*
To allow
Cross-origin resource sharing
X-XSS-Protection Mozilla
Stops pages from loading when they detect reflected cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks
Non standard, deprecated by Content-Security-Policy, but maybe useful for older browsers
Possible values:
0
- disables XSS filtering; never use!
1
- enable XSS filtering, sanitize, usually default in browsers
1; mode=block
- enable, block rendering of page
Recommended:
1
To silently filter XSS and not server as a simple test bed for XSS attacks
X-Content-Type-Options Mozilla
Prevents browser from MIME-type sniffing a response away from the declared ie trust the web server.
Possible values:
nosniff
- prevents browser from MIME-type sniffing a response away from the declared content-type.
Recommended:
nosniff
Good additional information on attacks mitigated (MIME Confusion Attack, Unauthorized Hotlinking)
stackoverflow
X-Frame-Options Mozilla
Indicate whether or not a browser should be allowed to render a page in a <frame>, <iframe> or <object>
Non standard, deprecated by Content-Security-Policy, but useful for older browsers
Possible values:
deny
- no frames
sameorigin
- allow frame from origin
allow-from https://example.com/
- one domain
Recommended:
If you have no iframes, then
deny
If you want your content iframed in by multiple websites, then do not send this header
Strict-Transport-Security Key CDN
Restricts web browsers to access web servers solely over HTTPS; header only has effect when requested over HTTPS
Possible values:
max-age
- defines the time in seconds for which the web server should only deliver through HTTPS.
includeSubDomains
- optional, apply to subdomains
preload
- optional, the site owner can submit their website to the preload list which is a list of sites hardcoded into Chrome as being HTTPS only; Additional details
serverfault
Recommended:
If your site and all resources (images, javascript, css, etc) are available over HTTPS, as they should be, then enable; If you have mixed content, HTTP and HTTPS, then do not use this header
Given that browser will cache this header for your site, to test implementation, bump max-age up incrementally over time eg 300s=5min, 86400s=1day, 63072000s=2years required for preload
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=300; includeSubDomains
Good additional information on why to use it
stackoverflow, and what to be careful of
stackoverflow
Referrer-Policy ScottHelme
Determine what information about the origin the user came from is sent to the destination site
Possible values:
no-referrer
- not referrer sent
no-referrer-when-downgrade
- do not send the referrer header when navigating from HTTPS to HTTP
same-origin
- only set the referrer header on requests to the same origin
origin
- set the referrer header to the origin, stripping any path information
strict-origin
- same as origin, but do not send HTTPS request on HTTP
origin-when-cross-origin
- send the full URL to requests to the same origin but only send the origin when requests are cross-origin
strict-origin-when-cross-origin
- same as origin-when-cross-origin, but do not send when navigating from HTTPS to HTTP
unsafe-url
- always send the referrer; do not use!
Recommended:
no-referrer-when-downgrade
To prevent any HTTPS info (referrer url) being sent over HTTP
Content-Security-Policy Key CDN Mozilla
Content-Security-Policy (CSP) is an added layer of security that helps to detect and mitigate certain types of attacks, including Cross Site Scripting (XSS) and data injection attacks. It replaces several of the above X- headers, but support depends on browser and browser versions, so you should still the above headers.
CSP makes it possible for server administrators to reduce or eliminate the vectors by which XSS can occur by specifying the domains that the browser should consider to be valid sources of executable scripts. A CSP compatible browser will then only execute scripts loaded in source files received from those white listed domains, ignoring all other script.
Note: While searching for CSP policy values, remember CSP version 2 is currently defined, and CSP version 3 is in the works. Across the versions, policy values have been added and removed, thus support depends on browsers and browser's versions.
An example Content-Security-Policy:
Content-Security-Policy "base-uri 'self'; object-src 'none'"
Possible policy keys:
default-src
- default policy for all resources type that are not defined (fallback)
script-src
- which scripts the protected resource can execute
object-src
- from where the protected resource can load plugins (flash, java, etc)
style-src
- which styles (CSS) the user applies to the protected resource
img-src
- from where the protected resource can load images
media-src
- from where the protected resource can load video and audio
frame-src
- from where the protected resource can embed frames
frame-ancestors
- valid parents that may embed a page using <frame>, <iframe>, <object>, <embed>, or <applet>
font-src
- from where the protected resource can load fonts
connect-src
- which URIs the protected resource can load using script interfaces
form-action
- which URIs can be used as the action of HTML form elements
script-nonce
- script execution by requiring the presence of the specified nonce (cryptographic number used once) on script elements
report-uri
- Specifies a URI to which the user agent sends reports about policy violation
Deprecated keys (you may run across in searches, but don't use)
reflected-xss
- instructs a user agent to activate or deactivate any heuristics used to filter or block reflected cross-site scripting attacks, equivalent to the effects of the non-standard X-XSS-Protection header
referrer
- determine what information about the origin the user came from is sent to the destination site
Possible values:
blobfolio
*
– wildcard, i.e. anything goes
'none'
– load no resources
'self'
– same-origin is OK
data:
– data-URI, such as a base64-encoded image
https:
– any resource over HTTPS
domain.com, *.domain.com, https://domain.com
– domain.com (any protocol), all subdomains of domain.com (any protocol), domain.com (SSL) respectively
For scripts and stylesheets specifically, there are a few additional magic values:
'unsafe-eval'
– allow scripts to run eval().
'unsafe-inline'
– allow all inline scripts and/or styles.
'nonce-XXX'
– allow inline or linked assets with the nonce
stackoverflow
For more options and information refer to
Mozilla
Recommended values:
A minimal CSP which should not break stuff is:
Content-Security-Policy base-uri 'self'; object-src 'none'
This ensures your base uri is not change via html injection, and that your site does not allow flash or applets
Adding CSP does require you know your application or websites resources, which may be non trivial.
Adding CSP can break you application or website, by preventing resources from loading.
For example,
object-src 'none' disable embedded pdfs in Chrome.
Testing, as always, is important. To facilitate testing, consider adding one policy at a time.
Example Content-Security-Policy of a few domains:
google.com
header not set
amazon.com
header not set
aws.amazon.com
header not set
mail.google.com
script-src 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval' https: http:;object-src 'none';base-uri 'self';report-uri /cspreport
securityheaders.com
default-src 'self'; script-src 'self' cdnjs.cloudflare.com; img-src 'self'; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline' fonts.googleapis.com cdnjs.cloudflare.com; font-src 'self' fonts.gstatic.com cdnjs.cloudflare.com; form-action 'self'; report-uri https://scotthelme.report-uri.com/r/default/csp/enforce
msn.com
default-src 'self' data: 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval' https: blob:; media-src 'self' https: blob:; worker-src 'self' https: blob:; block-all-mixed-content; connect-src 'self' data: 'unsafe-inline' 'unsafe-eval' https: blob: https://*.trouter.io:443 https://*.trouter.skype.com:443 wss://*.trouter.io:443 wss://*.trouter.skype.com:443;
stackoverflow.com
upgrade-insecure-requests
Given that CSP is non trivial and policies can break the app, consider adding
report-uri "/csp-report-violation"
or use the free service
report-uri
report-uri "https://report-uri.io/"
and view the results in developer tools and/or log the results
{"csp-report": {
"document-uri": "https://example.com/signup.html",
"referrer": "",
"blocked-uri": "http://example.com/css/style.css",
"violated-directive": "style-src cdn.example.com",
"original-policy": "default-src 'none'; style-src cdn.example.com; report-uri /_/csp-reports",
"disposition": "report"
}}
To test your changes, load you application or website in a browser and view the developer tools network tab and review the headers.
For nicer graphical view, with a warm fuzzy grade system, which others might use, visit
securityheaders.io
Examples of how to add the HTTP Security Headers
PHP:
header("X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff");
header("X-XSS-Protection: 1");
header("X-Frame-Options: sameorigin");
header("Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=31536000s; includeSubDomains");
header("Referrer-Policy: no-referrer-when-downgrade");
header("Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *");
header("Content-Security-Policy: base-uri 'self'; object-src 'none'");
PHP framework/library:
$response->headers->set('X-Content-Type-Options', 'nosniff');
$response->headers->set('X-XSS-Protection', '1');
$response->headers->set('X-Frame-Options', 'sameorigin');
$response->headers->set('Strict-Transport-Security', 'max-age=31536000s; includeSubDomains');
$response->headers->set('Referrer-Policy', 'no-referrer-when-downgrade');
$response->headers->set('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
$response->headers->set('Content-Security-Policy', "base-uri 'self'; object-src 'none'");
Apache config/.htaccess:
Header set X-Content-Type-Options nosniff
Header set X-XSS-Protection 1
Header set X-Frame-Options sameorigin
Header set Strict-Transport-Security max-age=31536000s; includeSubDomains
Header set Referrer-Policy no-referrer-when-downgrade
Header set Access-Control-Allow-Origin *
Header set Content-Security-Policy "base-uri 'self'; object-src 'none'"
nginx config
add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff
add_header X-XSS-Protection 1
add_header X-Frame-Options sameorigin
add_header Strict-Transport-Security max-age=31536000s; includeSubDomains
add_header Referrer-Policy no-referrer-when-downgrade
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *
add_header Content-Security-Policy "base-uri 'self'; object-src 'none'"
-End of Document-
Thanks for reading